The archaeologist brings to light and studies in great detail the ancient objects that are hidden either under the earth surface or into the sea bottom. He or she tries to understand and interpret the civilizations of past societies, where from come the finds he or she uncovered in their land or underwater research.
The ship, which sank at Antikythera sometime between 75 – 50 B.C., was a freighter, its estimated capacity being 300 tons.
The vessel was heading toward its destination most probably in Italy and sank northeast of Antikythera.
In that era, the political, economic and social situation in east Mediterranean was particularly fluid. The desire of the Roman ruling class for luxury objects from the Near and Middle East contributed to the increase of seaborne trade products. In the same period, there is a widespread use of luxurious items and works of art for the decoration especially of private villas.
The location and retrieval of the Antikythera Shipwreck marks the beginning of underwater archaeology in Greece and on the basis of the evidence it brought to light a new approach to ancient Greek technology was introduced.
The objects the ship was carrying provide important evidence on the circulation of sculptures, jewellery, vases with their contents, utensils and coins during that particular period of time. The unexpected recovery of the Mechanism and the efforts to decode its intricate function render it unique as to its construction and function.
It was retrieved in two phases: the first one under the supervision of the Greek Archaeological Service in 1900/1901, with the contribution of sponge divers from Syme and of the Greek Royal Navy, and the second one in 1976, with the support of Jacques – Yves Cousteau’s oceanographic vessel «Calypso». The underwater research of the Antikythera shipwreck continues until today.
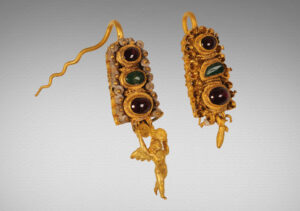
The most impressive part of the cargo includes: the original bronze statues of the “Youth of Antikythera” and the “Philosopher” along with the marble statues of Gods and Heroes, the Mechanism of Antikythera. Moreover, there were found bronze beds of exquisite art and quality, gold jewels, glass vases and various other utilitarian objects of the era, such as pointed transport amphorae, lagynoi/jugs and lamps for lighting the ship.
The Mechanism, a creation of the 2nd cent. B.C., comprises toothed gear wheels, axes, dials and pointers, made of copper sheets, with low content in tin (bronze).
It was contained into a wooden case and bore a metal plaque on the front and back side.
Its technology, which relates to the successors of Archimedes and the School of Poseidonios in Rhodes, was based on the knowledge of the Hellenistic period and manifests the astronomical, mathematical and engineering genius of the ancients in the mid 2nd cent. B.C., with a range of applications, as an instrument of scientific research, a means for the prediction of eclipses and a calendar, and probably an accessory of astrology and navigation.
























![Sponge divers off Antikythera (1900-1901) [NAM Photographic archive]. Glass negative inv. no. 1. Β1.2.3](https://antikythera-mechanism.namuseum.gr/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/anelkisi-08-300x194.jpg)
![Sponge divers off Antikythera (1900-1901) [NAM Photographic archive]. Glass negative inv. no. 1.Β1.2.4](https://antikythera-mechanism.namuseum.gr/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/anelkisi-09-300x169.jpg)
![Sponge divers off Antikythera (1900-1901) [NAM Photographic archive]. Glass negative inv. no. 1.Β1.2.1](https://antikythera-mechanism.namuseum.gr/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/anelkisi-10-300x169.jpg)
![Photo from the 1st phase of the shipwreck retrieval (1900-1901) [NAM Photographic archive]. Glass negative inv. no. 1.Β1.2.9](https://antikythera-mechanism.namuseum.gr/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/anelkisi-11-300x169.jpg)






